Managing the revenue processes is essential for any organization’s financial well-being. Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is the spine of a healthcare organization’s financial operations, bridging the gap between patient care and business aspects. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its significance, workflow, and tips for optimization.
What is Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare?
Revenue cycle management (RCM) is the process healthcare organizations use to track revenue growth from patients from their first appointment or engagement with the healthcare system to their payment of any outstanding debt.
The appointment or hospital visit initiates the revenue cycle process, which concludes when the hospital or provider fully compensates for the services rendered.
Healthcare organizations that track patient care from registration to final payment collection employ revenue cycle management (RCM). Healthcare providers can identify, collect, and manage payer revenue through RCM. These payers include patients, private insurers, and government insurers like Medicare and Medicaid.
Significance of RCM in Healthcare

According to data from Data Bridge Industry Research, the revenue cycle management (RCM) industry, valued at USD 46.62 billion in 2022, would grow to USD 133 billion by 2030 and have a CAGR of 14% from 2023 to 2030.
Saving time
By optimizing processes, such as patient pre-registration and registration, appointment and payment reminders, and engaging payors with claims and denials, RCM aids companies in saving time.
Minimize mistakes
RCM can help hospitals and health systems identify mistakes early so they may be rapidly fixed.
Reduce expenses
Organizations can cut the costs related to managing their income with less time investment and a lower risk of mistakes.
Fewer denials
RCM can speed up payments to the organization by lowering the denial rate and minimizing or eliminating errors in payment claims.
Less administrative burden
By easing the administrative effort associated with creating invoices, reporting claims, and collecting payments, effective RCM can hasten the collection process.
Better patient experience
RCM simplifies and streamlines the revenue process, allowing hospitals and health systems to focus more on delivering quality care and an optimal end-to-end patient experience.
Revenue Cycle Management Process Workflow
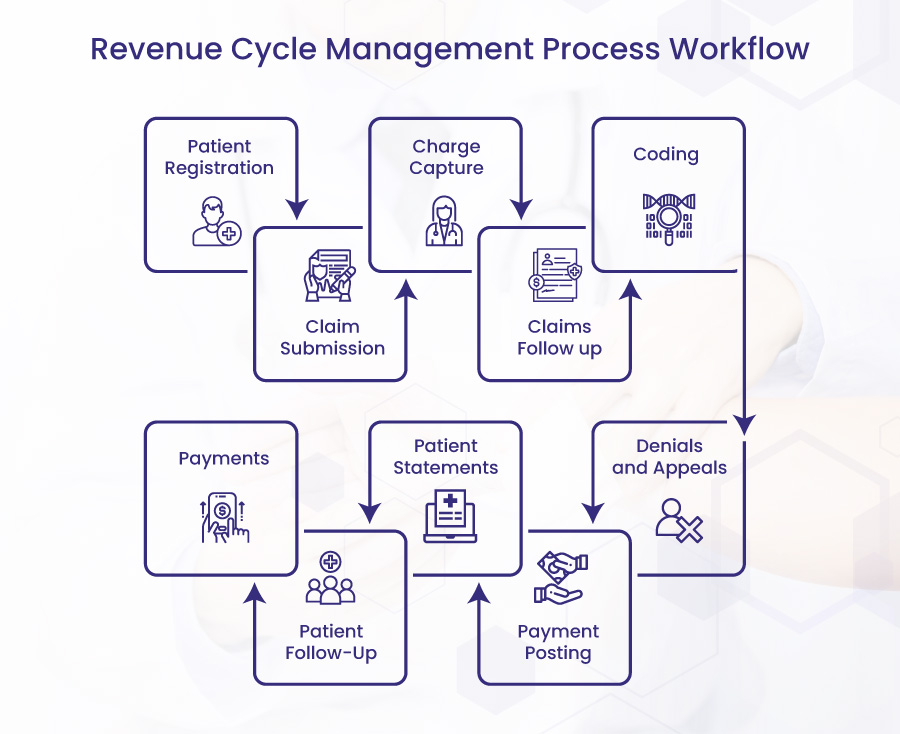
Patient Registration
The revenue cycle management process begins when patients schedule an appointment with the healthcare practice. Both new and returning patients should be able to be handled by the front desk. For instance, if patients are particular, they carefully gather demographic data about them and confirm their insurance.
The insurance provider will deny the claim if the desk makes mistakes. You should double-check the information and advice returning patients of their outstanding balances if they’ve made modifications.
Charge Capture
The clinician records the visit in the patient’s electronic health record (EHR) after the patient attends appointments. Patient history, encounter notes, diagnosis codes, follow-up data, orders, medicines, assessments, and lab results are all included in the record.
Coding
The medical coding team records the diagnosis, healthcare standard procedure coding system (HCPCS), and current procedural terminology (CPT) codes based on clinical documentation. Depending on the payer and the CPT code for the procedure, the coder may also add a modifier. Knowing payer policies and claim specifications is crucial to ensuring payment for the service or interaction.
Claim Submission
The billing team enters the claim’s charges on a CMS-1500/UB-04 form or a medical billing system. The team then creates the claim in the provider’s EHR and sends it electronically or on paper to the clearinghouse (public or private payers may provide insurance). The payer receives the claim from the clearinghouse, who may reject it. If the clearinghouse denies the claim, the billing team may locate and fix the underlying issue. The staff can reprocess and resend the claim to the payer once they identify the problem.
Claims Follow up
The back-end staff will keep track of the date the practice submitted the claim and check on its status. This group includes billing specialists and accounts receivable. A follow-up should occur at least once every 30 days until the payer pays the claim. The practice may occasionally need to make its claim follow-up process more frequent.
Denials and Appeals
The billing team will address denials by locating the underlying issue and filing a revised claim, a reconsideration request, or an appeal. The billing team will then check on the denial status after that. The insurer will post payment if it reverses its first claim denial. The appeals procedure is repeated if the payer continues to reject the claim. The healthcare provider may opt to write off the claim as a loss if the payer does not alter their mind after going through the process.
Payment Posting
The billing department will input payer reimbursement into the medical billing system. This gives an overview of the financial situation of healthcare providers.
Patient Statements
Medical bills are prepared and sent to the patient after entering information into the medical billing software. Modern billing software can make this step automatic. The medical bill includes all expenses for which the patient is deemed liable.
Consider the patient’s preferred method of communication when sending statements: text, email, or paper. Finding the correct channel can help patients become more financially engaged and increase the likelihood of paying their bills on time.
Patient Follow-Up
Many patients cannot pay the remaining debt when they receive a statement for their medical expenses. This is primarily the result of misunderstandings about benefits, rejected claims, expensive service costs, or other financial troubles.
When a patient owes a balance, the healthcare practitioner must contact them to get the money.
Payments
You’ll receive service payments once you’ve followed up with patients and completed the insurance reimbursement process.
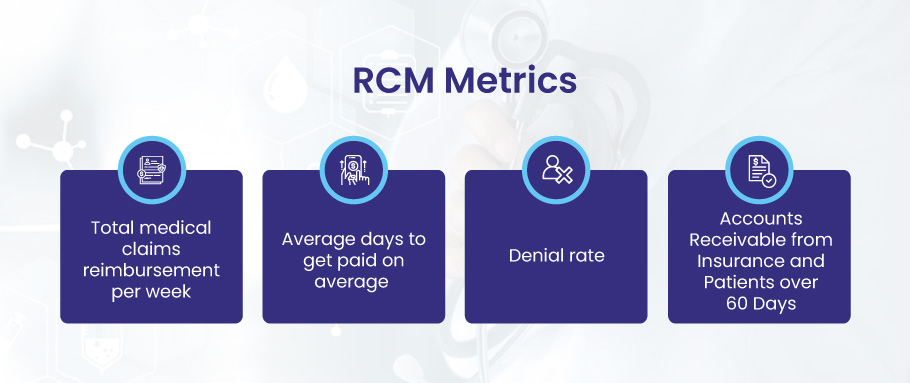
RCM Metrics
- Total medical claims reimbursement per week
- Average days to get paid on average
- Denial rate, and
- Accounts Receivable from Insurance and Patients over 60 Days
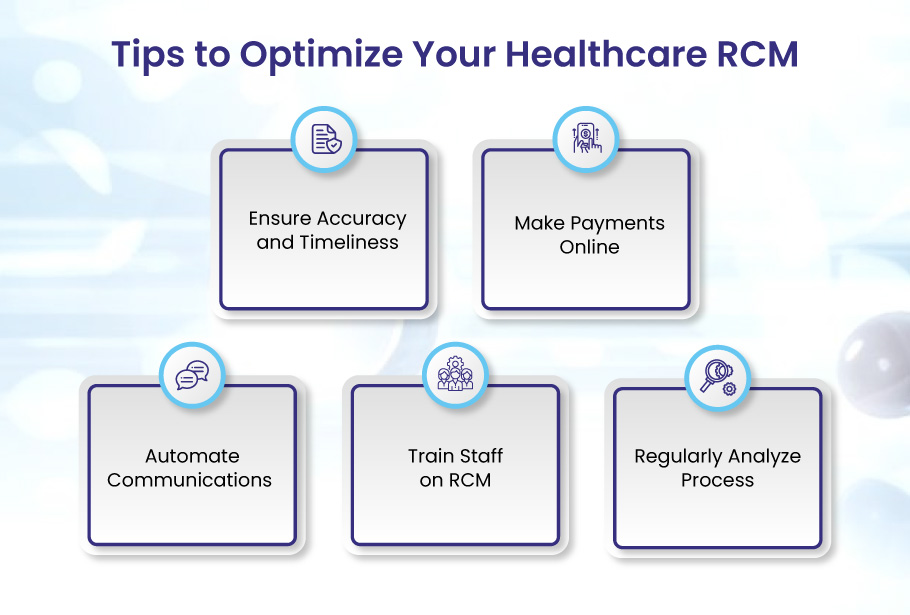
Tips to Optimize Your Healthcare RCM
Effective Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in the healthcare sector is challenging and crucial for the overall performance of your practice. RCM helps increase performance, the administration burden decreases, and profits can rise. As a result, improving RCM processes offers a fantastic chance to increase investment returns and operational efficiency in any hospital environment. Let’s discuss the tips to enhance the revenue cycle.
Ensure Accuracy and Timeliness
The practices and healthcare providers must not underestimate the significance of revenue cycle management RCM. They need to track the shortcomings of it and fix them swiftly. Accuracy and time are significant aspects that positively affect streamlining the RCM process. Ensure Accuracy in the payment process, correctly record the patient information, and follow the timeframe to submit the claims. This will help facilitate the RCM process, leading to overall patient satisfaction and maximum financial growth of your practice.
Make Payments Online
Online payment system ensures security and accuracy in the payment posting process. It also helps reduce paperwork and administrative burden. Through portals, practices can easily update and provide patients access to crucial medical information and treatment plans.
The move to totally electronic transactions could cut yearly healthcare costs by 41%, according to the 2022 CAQH Index. Even while RCM operations may not yet be entirely computerized, using SaaS software to streamline them could boost providers’ income.

For an efficient RCM process, providers must employ online patient portals to transfer payments. Secure payment posting and transactions may boost your practice’s RCM workflow and help maximize collections.
Automate Communications
Communication plays a vital role in maintaining RCM workflow. Practices and doctors must automate their communication process when collaborating with patients and insurance providers. To automate communications, practices can employ advanced tools such as Practice Management Systems, Patient portals, and emails. Prompt communication with patients and insurers can help resolve issues like payment processing, providing patients with essential information, and remaining updated with the insurance company’s updates can help keep the RCM process on track and streamlined.
Train Staff on RCM
Training staff is also essential for providers for a successful RCM workflow. A well-trained and knowledgeable staff can implement the best practices to streamline the billing process by accurate claim submission, ensuring correct coding, properly managing the denials, and maximizing overall collections. The practices must train the staff on HIPAA regulations, coding systems like ICD-10 and ICD-11, and the latest technological innovations in healthcare. This will help boost the overall efficiency of the RCM process, leading to the practice’s sustainability and profitability.
Regularly Analyze Process
Analyzing the revenue cycle management process can help healthcare providers make proactive decisions to optimize the processes. Practices and providers must identify the factors causing the instability in the RCM workflow and promptly fix them to make the process successful. Ensure ongoing processes like patient information, medical coding, claim follow-ups, and denials are monitored. This helps them eliminate errors, provide updated and correct information, and properly deal with denied claims.
Conclusion
Revenue Cycle Management is not just a financial process but an art that requires precision, promptness, and efficiency. As healthcare evolves, the challenges in RCM are bound to increase. However, with a clear understanding of its processes, regular training, efficient communication, and advanced technologies, healthcare providers can simplify the intricate maze of RCM. This will ensure maximum revenue realization, reduced administrative burdens, and enhanced patient experiences. By investing time and resources into mastering RCM, healthcare institutions lay down a strong foundation for their future growth and sustainability.




