Medicaid is a government-funded healthcare program that provides medical assistance to low-income individuals and families in the United States. With over 70 million people enrolled, it’s crucial for healthcare providers to become credentialed with Medicaid to get authorized to provide care according to the healthcare standards and expand their patient base.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the process of credentialing with Medicaid and discuss its importance for healthcare providers.
What is Provider Credentialing in Healthcare?
Physician credentialing has been in practice since 1000 BC, but it has surely evolved ever since. Credentialing is a process that involves the verification of the qualification, experience, and skills of a practitioner and authorizing him to deliver healthcare services in his healthcare network.
It’s essential to note that insurance companies are most likely to pay for the services provided by credentialed practitioners. Therefore, it’s crucial for your practice to get licensed to practice care.
The competency of a healthcare physician is checked through the following measures:
- Complete qualification & transcripts
- Complete professional history
- Medical license, board certification, & DEA registration
- Up-to-date personal health history & immunization records
- Proof of continuous malpractice coverage
- Personal & professional references
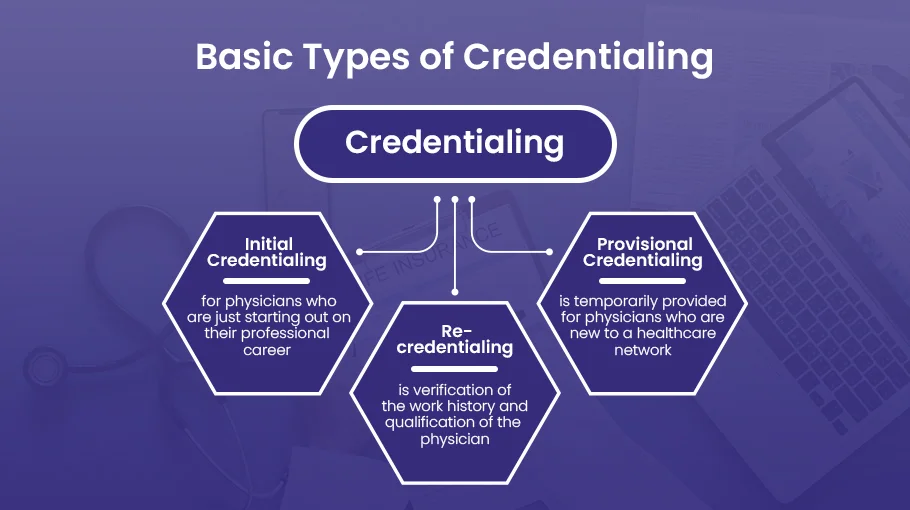
Types of Medical Credentialing
There are generally three types of medical credentialing services for physicians, namely:
- Initial Credentialing
- Re-credentialing
- Provisional Credentialing
Now the type of credentialing you need depends upon your practice and career type. Let’s look at each one in more detail for you to figure out your credentialing needs.
Initial Credentialing
Initial credentialing is for those physicians who are just starting out on their professional career in the healthcare industry. It includes verification of the qualifications and background of the new professionals.
Re-credentialing
Re-credentialing is the process of verifying the work history and qualification of the physician. It is done to ensure his care quality is up to date and meets the necessary healthcare standards.
Provisional Credentialing
Provisional credentialing is provided to physicians who are new to a healthcare network. It is provided temporarily.
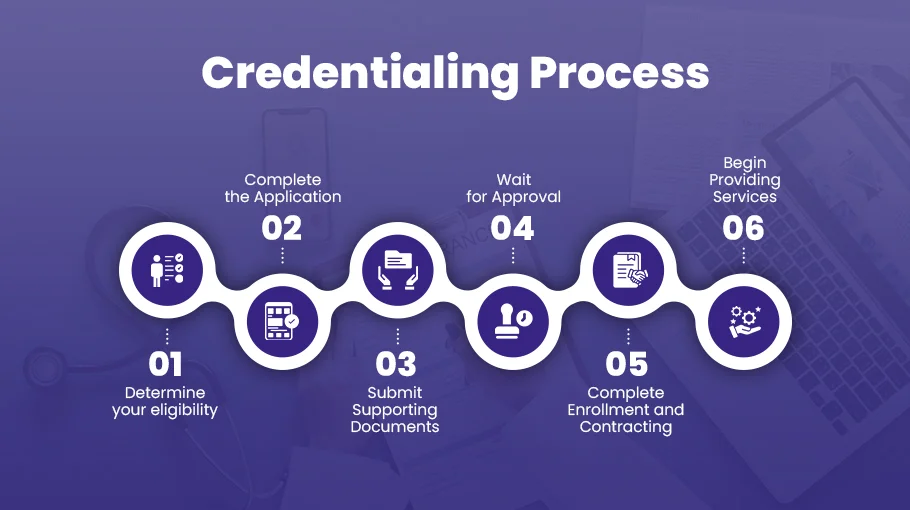
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Credentialed with Medicaid
Determine your eligibility
Before you begin the credentialing process, it’s important to determine your eligibility. To participate in Medicaid, you must:
- Be a licensed healthcare provider enrolled in Medicare or eligible to enroll.
- Have a National Provider Identifier (NPI) number and a Tax Identification Number (TIN).
Complete the application
Once you have determined your eligibility, you can begin the application process. The application for Medicaid credentialing varies by state, so you should contact your state’s Medicaid agency to obtain the appropriate forms and instructions.
The application will generally require information about your practice, such as your NPI and TIN numbers, business name and address, and license information. You will also need to provide information about your education, training, and experience, and any malpractice claims or disciplinary actions taken against you.
Submit supporting documents
Along with your application, you must submit supporting documents, such as copies of your license, malpractice insurance, and DEA registration. You may also need to document your education, training, and experience. It’s essential to ensure that your supporting documents are current and accurate. Any discrepancies or incomplete information can delay the credentialing process.
Wait for approval
Once you have submitted your application and supporting documents, you must wait for approval. The time it takes to get credentialed with Medicaid varies by state, ranging from a few weeks to several months. During this time, you may be contacted by the Medicaid agency for additional information or to schedule a site visit to your practice.
Complete enrollment and contracting
After you have been approved for Medicaid credentialing, you will need to complete the enrollment and contracting process. This involves signing a provider agreement with the Medicaid agency and agreeing to comply with all program requirements, such as submitting claims for covered services and maintaining accurate patient records. Depending on your state’s Medicaid program, you may also need to complete additional training or education requirements.
Begin providing services
Once you have completed the enrollment and contracting process, you can begin providing services to Medicaid patients. It’s important to ensure you understand the program requirements and billing procedures to ensure you are reimbursed correctly for your services.
The Importance of Medicaid Credentialing for Healthcare Providers
Increased patient volume
By participating in Medicaid programs, healthcare providers can increase patient volume. Medicaid beneficiaries often face difficulties in accessing healthcare, and by becoming a Medicaid provider, healthcare providers can reach out to these patients and provide them with much-needed care.
A steady stream of revenue
Credentialing with Medicaid also ensures a steady revenue stream for healthcare providers. Medicaid reimburses healthcare providers for services rendered to beneficiaries. By becoming a Medicaid provider, healthcare providers can access a reliable source of revenue.
Access to additional resources
Medicaid credentialing also provides healthcare providers with access to additional resources. Medicaid programs often offer educational opportunities, training, and other resources that healthcare providers can use to improve their skills and provide better care to patients.
Improved patient outcomes
Medicaid programs are designed to improve patient outcomes by ensuring beneficiaries have access to quality healthcare. By participating in Medicaid programs, healthcare providers can contribute to this goal and improve patient outcomes.
Increased professional credibility
Credentialing with Medicaid also increases a healthcare provider’s professional credibility. Medicaid programs have strict standards for credentialing, and by meeting these standards, healthcare providers demonstrate their commitment to providing quality care to patients.
Access to a large patient population
According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, over 68 million individuals were enrolled in Medicaid and CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program) in 2020. By getting credentialed with Medicaid, you can provide healthcare services to this large patient population, including low-income families, pregnant women, and individuals with disabilities.
Reimbursement for services rendered
Getting credentialed with Medicaid is essential to ensure you get reimbursed for your healthcare services. Medicaid reimburses healthcare providers for the services they render to eligible beneficiaries. This means that by getting credentialed with Medicaid, you can receive payment for the services you provide to Medicaid beneficiaries.
Compliance with federal and state regulations
Credentialed healthcare providers must comply with federal and state regulations related to the Medicaid program. By getting credentialed with Medicaid, you will be required to comply with regulations related to billing, documentation, and other aspects of providing healthcare services to Medicaid beneficiaries. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid penalties, fines, and legal actions.
Increased revenue
Getting credentialed with Medicaid can also help you increase your revenue. By providing healthcare services to Medicaid beneficiaries, you can generate revenue you would not otherwise have. Medicaid reimbursement rates are generally lower than private insurance rates but can still help you increase your patient volume and overall revenue.
Expanded patient base
Getting credentialed with Medicaid can help you expand your patient base. Medicaid beneficiaries often need healthcare services and may not have access to private healthcare providers. By credentialing with Medicaid, you can provide services to this underserved population and expand your patient base.

How to Avoid Medical Credentialing Mistakes?
Medical credentialing mistakes can be lethal to your practice’s financial health. Practicing these mistakes can lead you to time and money penalties. Here’s how you can avoid credentialing mistakes in the healthcare industry
- Staying informed about credentialing updates is crucial to avoid any credentialing mistakes. Once you are aware of the procedure, steps, and requirements, you can process your credentialing according to the latest trends. Moreover, you can use credentialing software services to accelerate the process.
- To avoid credentialing mistakes it’s recommended to cross-check all your credentialing data. By double check all your credentialing information you ensure that the information provided is correct and up-to-date.
- Being more transparent in your credentialing process is the key to getting smooth credentialing. Be truthful about your work history and any malpractices or failings to avoid delays or rejections.
- Another common mistake you can avoid is avoiding communication. You have to maintain regular communication with the credentialing team to stay updated with the current trends as well as to avoid credentialing errors in your application.
- Getting organized is essential to your credentialing process. If you want to streamline your credentialing system, it’s important to maintain and update your documents, licenses, or registrations and make them easily accessible to the credentialing team.
Conclusion
Getting credentialed with Medicaid can be a complex and time-consuming process. However, it’s an important step for healthcare providers who want to expand their patient base and improve access to healthcare for low-income individuals and families.
By following these steps and working with your state’s Medicaid agency, you can become credentialed with Medicaid and start providing services to those in need. By doing so, you can enjoy the benefits of increased patient volume, revenue, access to resources, improved patient outcomes, and professional credibility that come with being a Medicaid provider.
At Bell MedEx we ensure that our credentialing services organize and manage physician applications to ensure that the credentialing process proceeds efficiently. Partner with BellMedEx and get your medical credentialing verified as soon as possible.




