In recent years, the field of Telehealth has emerged as a significant participant. Due to its convenience, accessibility, and capacity to stop transmitting contagious diseases, Telehealth has gained popularity among many medical offices and hospitals, especially after the COVID-19 outbreak worldwide.

Telehealth During COVID-19
- According to a survey, 85% of Indian physicians used telemedicine daily during the pandemic.
- According to McKinsey, the percentage of virtual visits in telemedicine increased from 11% in 2019 to 76% in 2020.
- A Merritt Hawkins survey found that 48% of healthcare professionals had opted to treat their patients via telemedicine.
- According to CDC.gov, compared to March 2019, telehealth visits increased by 154% in March 2020.
- According to a recent report, the worldwide telemedicine industry is projected to be worth USD 42.5 billion in 2021 and USD 73.2 billion by 2026, expanding at a CAGR of 11.5%.
In this blog, we will learn about telehealth and how it helps practices to improve medical operations.
What is Telehealth?
The delivery of medical services using technology is known as Telehealth or telemedicine. Today’s telehealth technologies can assist small clinics in giving their patients a high standard of care. Practices can use these technologies to become more productive and efficient than ever if they thoroughly understand them and everything they offer.

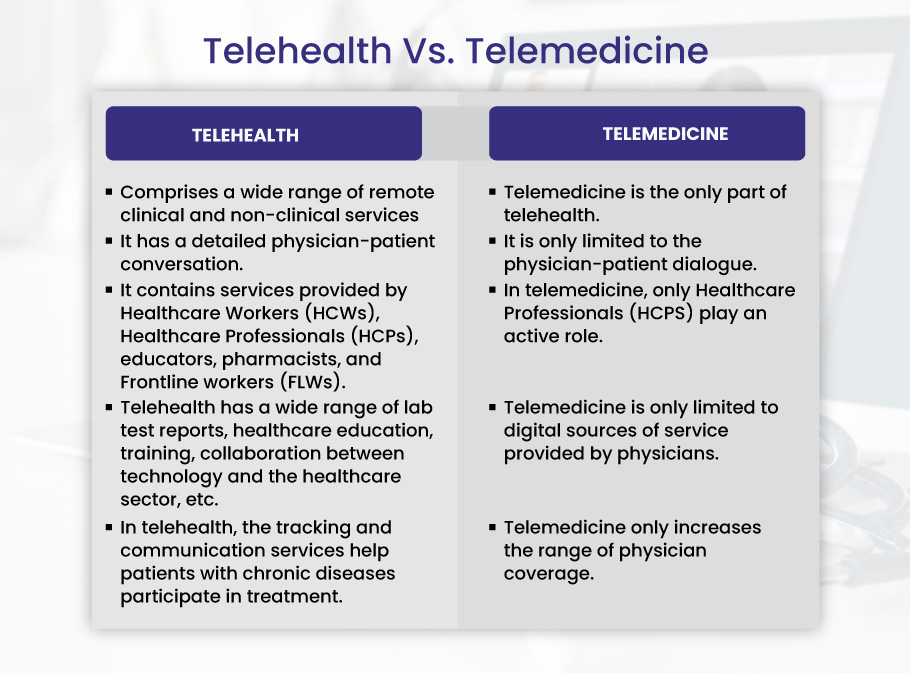
Telehealth Vs Telemedicine
Let’s understand the standard terms used in healthcare, such as telehealth and telemedicine.
Telehealth
Telehealth comprises various services that are rendered remotely. It does not have any patient-doctor relationship. Nurses, social workers, and pharmacists usually provide these services. For instance, they support patients and their carers in addressing health difficulties, social support, medication adherence, and patient health education.
Telemedicine
Telemedicine is the utilization of the latest technology for communication to deliver services related to medical, diagnostic, and treatment. Usually, doctors utilize telemedicine. For example, they check the patient’s treatment progress and conduct laboratory tests. The purpose of telemedicine services is to provide healthcare services to the patient at their doorstep.
Types of Telehealth/Telemedicine
Although many different forms of telehealth exist, three main types exist in today’s medical industry. The benefits of each category vary and can support you and your patients in different ways depending on what you need to get a full scope of their health.
Telehealth may have various types, but there are four main types in today’s healthcare landscape. Each type can benefit the patients and practitioners in different scenarios.
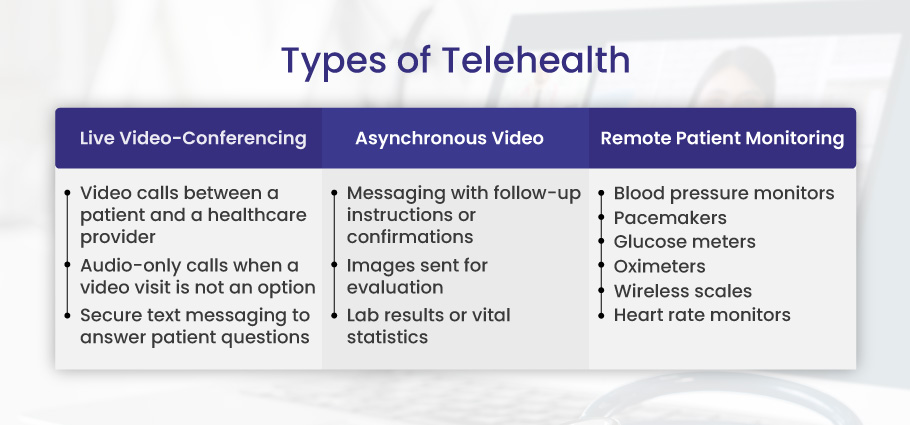
Three major telehealth types are:
- Live Video Conferencing
- Asynchronous Video (AKA Store-and-Forward)
- Remote-Patient monitoring
Live Video-Conferencing
Live video conferencing is a significant telehealth. It is also known as real-time interactive telemedicine. It is the most commonly used form of telehealth. As its name indicates, video-conferencing is a two-way—video-based interaction between a doctor and a patient. All practices, physicians, and hospitals can utilize it to deliver their services. Telemedicine helps minimize the time and distance to provide patient care. The patient-care services are delivered via messaging, phone, or video conferencing apps. The Physicians and practices provide video-conferencing care in case of emergency.
Asynchronous Video (Store-and-Forward)
Asynchronous is also known as store-and-forward telemedicine. This type of telehealth is also for rendering healthcare services at patients’ doorstep where physicians are unavailable. It is usually used in rural areas without enough medical facilities. The medical data and patient documentation, such as images (MRI scans and X-rays), laboratory reports, sound and video studies, etc, are transferred electronically in this form. Electronic health records (EHRs) store and exchange patient data.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is also the most used type of telehealth. It is used to check the medical conditions of patients remotely using innovative medical equipment like wearable devices (heart monitors, skin patches, smart shoes, or smartwatches). This type usually helps providers examine the patients in case of chronic diseases like heart disease, asthma, etc.
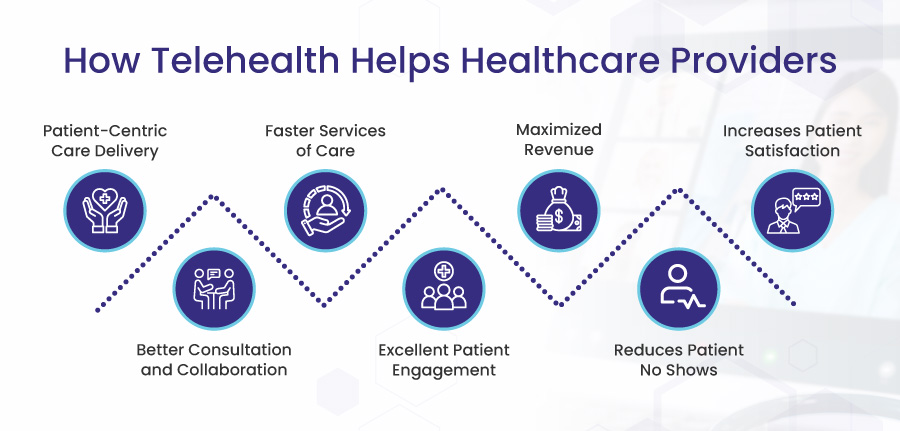
How Telehealth Helps Healthcare Providers
Telehealth simplifies the care delivery process for practices and healthcare providers. It is a rapid way to provide the services at the patient’s doorstep. As a result, they can carry out maximum checkups, boosting revenue collection.
Here’s how telehealth helps healthcare providers.
Patient-Centric Care Delivery
Patient-centric care delivery is an essential factor for providers. Telehealth enables them to provide online services with the help of teleconsultation solutions. Telehealth also helps integrate patient records into electronic health records (EHRS) to provide patients with seamless information and timely access to their needs. In this way, telehealth ensures patient-centric care delivery, making practice efficient and trustable among the patients.
Better Consultation and Collaboration
Telehealth has transformed the way of healthcare delivery. It has made the collaboration and consultation process more efficient and seamless. Doctors, nurses, and patients can collaborate. For example, telehealth helps them collaborate in the follow-up process. Additionally, in the consultation process, telehealth provides real-time access to doctors, allowing patients to consult with them on complex issues without hassle.
Faster Services of Care
Providing fast healthcare delivery is also essential for practices covering a wide range of areas, especially providing care to patients residing in remote areas. Telehealth has reduced the distance from patients to doctors or doctors to patients, as physical presence is no longer essential. Doctors can contact their patients remotely using video-conferencing and other sources to check and provide them with prescriptions and medications. Due to this, healthcare delivery has become fast, thanks to telehealth in healthcare.
Excellent Patient Engagement
Patient engagement is crucial for the success of medical practice. Telehealth empowers patients to remain engaged using innovative tools like smartphones, computers, and other digital devices. These devices help them book online appointments, take consultations, make payments, etc. Patient engagement with doctors becomes more convenient and seamless by using telehealth technology to make audio calls or video conferencing. The patients can share and consult on the medical test reports with the physician. They can also download medical reports using these platforms for future use. Finally, we can say that telehealth has dramatically enhanced patient engagement.
Maximized Revenue
The ultimate objective of telehealth is to lower the overall cost of care. As telehealth enables doctors to connect with a new patient group outside their towns and cities, they can earn more money. Further, since teleconsultation makes it simple for patients to follow up, it may generate profits from clients who otherwise might not be interested in doing so if their health has improved. Additionally, telehealth’s facilitation of second viewpoints can result in a new source of income.
Consequently, by using these virtual solutions, healthcare professionals can observe a rise in the patient population.
Reduces Patient No Shows
No-shows by patients can have a significant negative financial and operational impact on healthcare services. According to hospital officials, the patient must be contacted again to reschedule any canceled visits. This consumes the extra time the employees would otherwise have freed up.
Thankfully, patients may view doctors’ availability and independently rearrange appointments thanks to the digital ease provided by telehealth. As a result, telemedicine gives both patients and doctors more flexibility.
Increases Patient Satisfaction
Telehealth’s virtual services facilitate the development of a solid doctor-patient relationship. Everything is convenient for patients, from making an online appointment to paying bills online. Patients who use these services save time during doctor appointments and money on travel costs. This may ultimately improve patient satisfaction by enhancing the overall patient experience.
Telehealth Reimbursement for Providers
In a KLAS-CHIME study from October of last year, over 50 percent of respondents from 104 healthcare organizations indicated that limits on reimbursement constrict their ability to expand telehealth services for patients. Medicare and Medicaid offer disparate degrees of flexibility, while private payers represent varying funding levels.
Telehealth Reimbursement
| Medicare | Medicaid | Private Payers |
| Medicare, which pays for care for patients who stand to gain the most from telehealth, will only make payments if the patient’s service location is in an HPSA or a non-metropolitan statistical area (MSA). Medicare has restrictions on the organizations and places that can offer telehealth services. The Telehealth Resource Center (TRC) has provided covered providers, locations, and service listings if you want further information. | Chiron Health claims that Medicaid programs in 48 states will pay for telehealth services delivered through live video systems. In contrast, RPM will be covered by 19 state Medicaid programs. Seven states permit payment for all three telehealth categories, while 12 state programs will fund store and send telehealth. Medicaid is more telehealth-friendly than Medicare, but the regulations controlling payment through state Medicaid programs vary greatly. When getting telehealth care, for instance, some states need the patient to be in a hospital rather than at home, and others demand that the patient be co-located with a licensed physician. | Although numerous states have passed telehealth parity laws, no federal requirement mandates private payers to reimburse for telemedicine services. Payers are required under parity regulations to pay for the same telehealth services as those delivered in person. Additionally, they mandate that payers pay for telehealth services at the same rate as in-clinic services. |
Final Thoughts
Telehealth is a rapidly expanding medical service that offers patients and physicians many advantages. The most effective methods for billing and coding will change as it develops. It could be challenging to follow the regulations for virtual visits. This is because they fluctuate constantly or may differ amongst payers. You must also perform in-person visits and other administrative duties in addition to that.



