Imagine a busy clinic where stacks of paper EOBs (Explanation of Benefits) are piling up on the billing manager’s desk. Every day they spend more time manually entering payment details, chasing down discrepancies, and trying to decipher handwritten notes from various insurance companies. It’s like trying to juggle flaming torching while riding a unicycle.
Now, picture the same clinic where payments are processed automatically, adjustments are clear and transparent and everything fits together like a well-oiled machine. That is the magic of ERAs.
In this blog we will learn what is ERA in medical billing and how its helps healthcare providers in cutting the gaps between payment processing and final transactions.
What is ERA In Medical Billing?
An Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) is the electronic format of file 835. It contains the claim details and essential documents related to payments like claim status, benefits coverage. Insurance providers usually issue ERAs to healthcare providers.
| Electronic Remittance Advice (ERA) or 835 file is the electronic remittance that explains the payer, payee, payment amount, and other identifying information about the payment. Additionally, it contains other information that resulted from the adjudication process, including denial information and adjustment reasons codes and amounts. |
According to adopted transaction standards and operating rules, an ERA is federally mandated for all HIPAA covered entities using electronic transactions such as healthcare plans, clearinghouses and healthcare organizations.
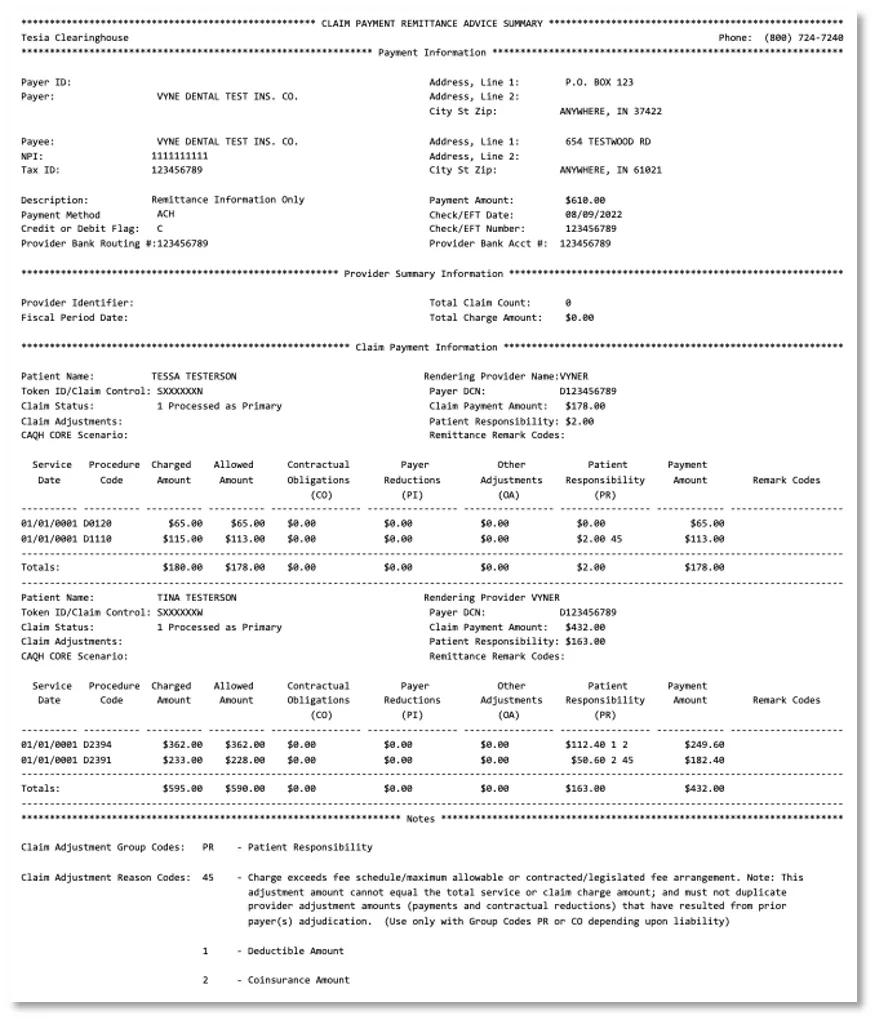
The ERA is transmitted in a HIPAA compliant ANSI X12 5010 format. Providers enrolled for 835/ERA are not eligible to receive Paper Remittance Advice by mail.
Standard Codes Used in ERA to Identify Adjustments
Providers can create the EOB as an electronic file, usually in a format called an 835, and can download the ERA 835 file from the clearinghouse.
The insurance providers itemize the claim details and status within an ERA. This itemized information helps providers to adjudicate with the claims.
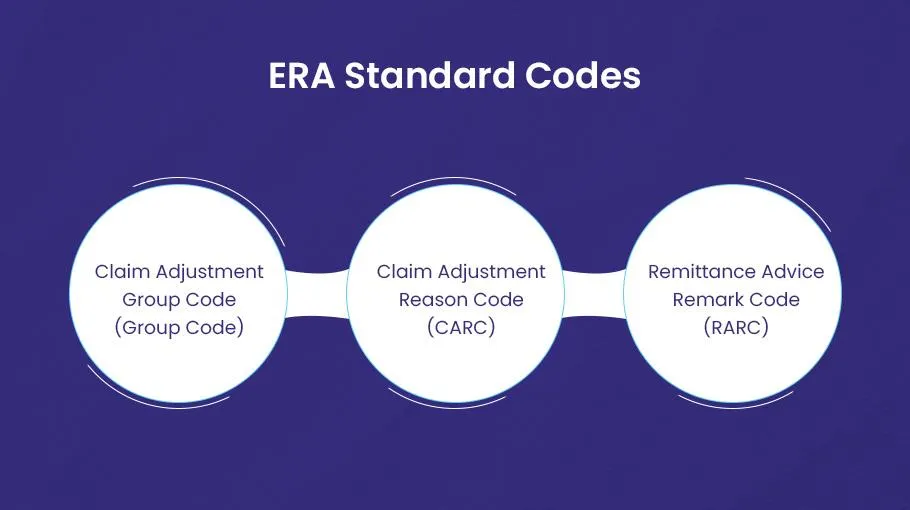
The ERA explains the reason and value of each adjustment. Adjustments appear claim wise or at a provider level at a line. Three standard codes identify the adjustment reasons in an ERA.
These codes are:
- Claim Adjustment Group Code (Group Code)
- Claim Adjustment Reason Code (CARC)
- Remittance Advice Remark Code (RARC)
Claim Adjustment Group Codes (Group Code)
Claim Adjustment Group Codes (Group Code) indicate and assign the responsibility of claim adjustment in the EOB. It comprises two alpha characters.
There are five Claim Adjustment Group Codes.
These include:
- Contractual Obligation (CO)
- Corrections and Reversal (CR)
- Other Adjustment (OA)
- Payer Initiated Reductions (PI)
- Patient Responsibility (PR)
It is worth mentioning that Medicare beneficiaries may be billed only when Group Code PR is used with an adjustment.
Claim Adjustment Reason Codes (CARCs)
The Claim Adjustment Reason Codes (CARCs) as name shows explain the reasons for the difference or mismatch in claims or services than they billed.
These codes are the standard way to transmit the information about adjustments made to a medical claim or a service.
The main objective of these codes is to provide a clear justification for any inaccuracy or a mismatch between the amount billed by the insurance provider and the amount billed by the healthcare provider.
Remittance Advice Remark Codes (RARCs)
Remittance Advice Remark Codes (RARCs) provide further details to an adjustment that is already explained by a CARC or to transfer information about remittance processing. Each RARC explains a specific message as given in the Remittance Advice Remark Code List.
Levels/Segments of an ERA
The electronic remittance advice (ERA) contains three levels.
- Header
- Details
- Remark
The items in the data record that contain ERA information are called segments, which are found in each ERA level.
An ERA’s general organizational structure is shown in the table.
| Header | Details | Trailer |
| The header contains: ◈ Payer tax ID ◈ Payee tax ID ◈ Personal information about the payer ◈ Payment data such as amount, method, and date ◈ Trace number | The detail provides an overview of the claim and adjustments. It contains: ◈ Benefits coverage ◈ Capitalization payments ◈ Contract agreements ◈ Copays and coinsurance ◈ Secondary payers | Finally, the trailer contains data about the following: ◈ Forwarding balance ◈ Overpayment recovery ◈ Capitation payments ◈ IRS levy |
How ERA Assists Providers in Payment Processing?
No doubt, utilizing innovative and cutting-edge solutions in healthcare can significantly benefit both providers and patients.
The electronic remittance advice (ERA) has made things more convenient for healthcare providers when they execute the payments workflow with payers.
Here are some major benefits of ERAs, how they help providers:
Minimizes Manual Processes
Traditional payment methods often involve cumbersome manual handling of documents such as Explanation of Benefits (EOB) statements, which are prone to errors and delays.
ERAs automate this process by electronically generating and transmitting these statements. This not only reduces the need for manual data entry but also minimizes the risk of lost or misplaced documents.
Providers can efficiently process ERAs through their practice management systems, automate posting payments, and apply standard adjustment reason codes directly to patient accounts. This reduces operational costs, saves time, and optimizes resource utilization, allowing staff to focus on more critical tasks.
Fast and Accurate Payments
ERAs significantly accelerate the payment process, leading to quicker and more accurate payments compared to traditional methods.
This improved speed can boost collections; reduce claim denials, and lower paper-related costs.
Enhanced payment accuracy and faster processing times contribute to smoother financial operations and improved overall productivity within healthcare practices.
Cuts Administrative Costs
By automating the billing and remittance process, ERAs reduce the administrative burden on healthcare staff.
The decreased need for manual paperwork allows staff to allocate more time to patient care.
Furthermore, ERAs help minimize human errors, which in turn reduces the frequency of claim denials and rejections, streamlining administrative tasks and improving overall efficiency.
Improved Patient Satisfaction
The efficiency brought by ERAs translates into a better billing experience for patients.
Faster, more accurate payments and clearer explanations of charges enhance billing transparency.
This improved communication not only builds trust but also fosters patient satisfaction and loyalty, positively influencing the patient-provider relationship.
Enhanced Workflow Efficiency
ERAs integrate seamlessly with revenue cycle management software, simplifying the payment process.
By eliminating the need for manual data entry into multiple systems, ERAs help reduce errors and save valuable time for billing staff.
Real-time access to ERA data enables healthcare practices to efficiently track claims, promptly address any issues, and maintain a smooth workflow.
Optimized Revenue Management
ERAs facilitate the swift identification of discrepancies in payments from insurance companies, ensuring accurate and full reimbursement.
Effective tracking of claim statuses and timely follow-ups on denied or rejected claims enhance revenue management and financial performance.
By addressing payment issues promptly, providers can improve their financial outcomes and maintain a healthier revenue cycle.
Final Thoughts
The ERA in medical billing marks a significant leap forward in the healthcare industry’s journey towards digital transformation. The ERAs have become indispensable tools for healthcare providers that optimize payment-posting workflows, enhance accuracy, reduce administrative burden and optimize the revenue cycle management.
Finally, they help providers maximize the revenue and patient satisfaction with fast and accurate payment transfers.




