The credentialing process with Medicaid can feel difficult at first.
But, don’t worry!
We’re here to help you every step of the way and make it super easy.
First things first, let’s talk numbers. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) reports that 76 million people are now enrolled in Medicaid. That’s a huge jump from May 2021, which had almost 75,888,651 enrollees! Many Americans depend on Medicaid for their healthcare, so it’s important for providers like you to be properly credentialed to help this growing group.
In this blog, we’ll explain the Medicaid credentialing process step by step. We’ll talk about why this is important, what mistakes to watch out for, and provide you with a simple, step-by-step guide to get your credentials fast and in line with the rules.
By the end, you’ll know everything you need to start accepting Medicaid patients confidently.
What is Medicaid Credentialing in Healthcare?
Medicaid credentialing is when healthcare providers show their qualifications, experience, and skills so they can serve Medicaid beneficiaries. By meeting Medicaid’s high standards, providers uphold the quality of healthcare services offered. Providers need the following for Medicaid credentialing:
- Send in proof of your education, like transcripts and residency certificates.
- Summarize your work history, including previous jobs and clinical experience, to show that you are reliable and capable.
- Make sure you hold a valid state medical license.
- Obtain board certification in their specialty area, like the American Board of Family Medicine for family practitioners.
- If you prescribe controlled substances, make sure to share your Drug Enforcement Administration Number (DEA).
- Show continuous malpractice insurance coverage for patient and provider protection.
- Offer references from colleagues, supervisors, or mentors to vouch for their qualifications and professionalism.
💡 Do You Know ➜ What is a DEA Number?
A DEA number is a special ID given to healthcare providers by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) for Medicaid credentialing.
It authorizes them to prescribe or handle controlled substances. Medicaid and other payers need a valid DEA number when they credential providers who prescribe these substances.
Here’s an example of a DEA number: AB1234567
| Here’s what the letters signify: 1️ First Letter (A/B/F/G/M): Indicates the type of registrant ➜ A/B/F/G: Practitioners (e.g., physicians, dentists). 2️⃣ M: Mid-level practitioners (e.g., nurse practitioners, physician assistants). 3️⃣ Second Letter: Corresponds to the first letter of the registrant’s last name (or business name for organizations). 4️⃣ Numbers (7 digits): A unique serial number for the registrant. |
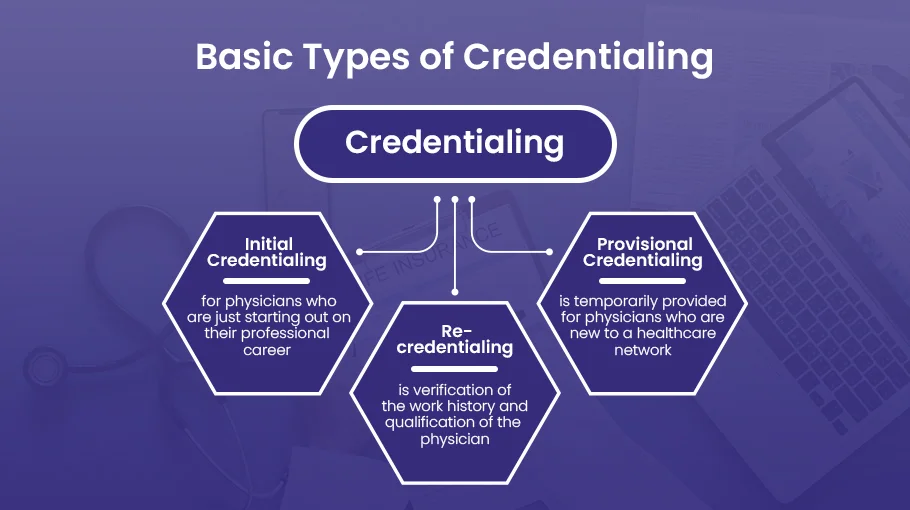
Types of Medicaid Credentialing
Each type of credentialing has a specific purpose. It ensures that healthcare providers are qualified and capable of delivering quality care to Medicaid beneficiaries. We’ve put together a list of different types of Medicaid credentialing to help you understand better:
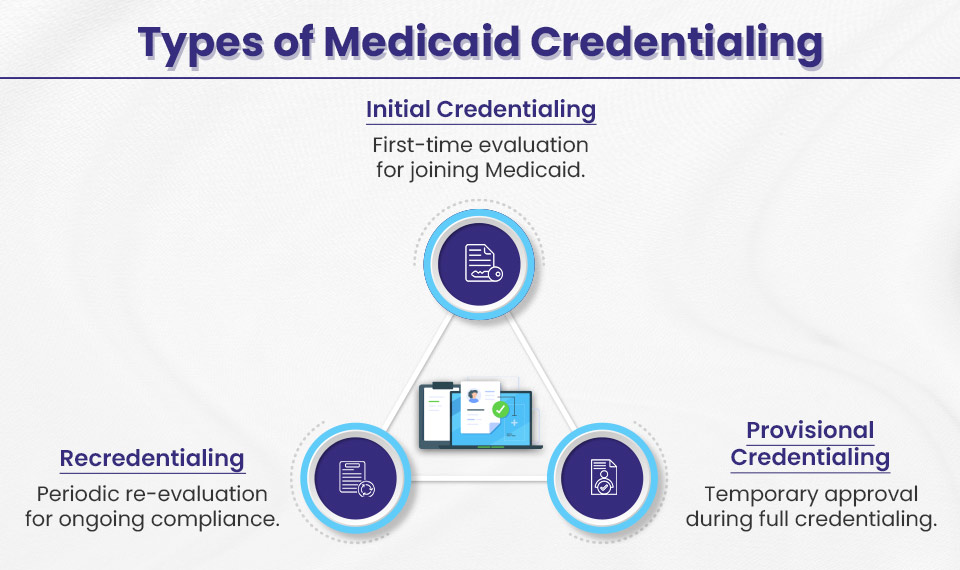
Initial Credentialing
This is for anyone who is just starting out or joining a new network. Before you can treat Medicaid patients, you’ll need to meet their initial credentialing requirements. Basically, you’ll need to submit things like your medical school transcripts, licenses, certifications, and board credentials. Once you get that Medicaid number, you’re good to go!
Re-credentialing
This is like a checkup for your credentials. Every 3 to 5 years, Medicaid checks to see if you still meet their standards and keep your qualifications current. Make sure to renew your licenses and certifications, and prove that you’ve been staying current with your continuing medical education (CME) credits. They will check your performance reviews and patient satisfaction surveys to ensure you are providing quality care.
Provisional Credentialing
This is the “let’s get you started” option. If you need to see Medicaid patients quickly, you can get provisional credentialing while your full application is being processed. It’s a temporary approval based on an initial review of your qualifications. During this time, they’ll keep a closer eye on you to make sure you’re following Medicaid’s standards. Once your full credentialing is complete, you’ll get that permanent Medicaid provider number, and you’re officially part of the program.
Step-by-Step Guide to Getting Credentialed with Medicaid
Now that we’ve talked about the different types of Medicaid credentialing, let’s dive into the entire Medicaid credentialing process. Understanding the step-by-step process to credential with Medicaid is important. This guide helps you understand the specific requirements, documents, and timelines for caring for Medicaid patients.

Step #1: Understand Your State’s Medicaid Requirements
The first step to getting credentialed with Medicaid is to understand your state’s specific requirements. While Medicaid programs have some commonalities across states, each one manages their own processes and eligibility criteria.
To get started, you’ll want to gather:
- Copies of your current, valid professional licenses and certifications
- Proof of your up-to-date liability insurance coverage
- Your National Provider Identifier (NPI) and Tax ID numbers
- Details about your practice – specialty, services offered, location, patient demographics, etc.
- Some states require additional items like background checks or fingerprinting. Contact your state Medicaid office to confirm their full list of requirements.
Having all of these items ready will make the application process smoother. Reach out to our credentialing specialists if you need help understanding your state’s specific Medicaid credentialing rules and documents. We’re here to help you prepare a complete application from the start.
🔵 What are the Requirements for Out-of-State (OOS) Medicaid Provider Enrollment?
If you’re a provider from another state wanting to enroll in Medicaid, here’s what you need to know:
➜ You have to meet the same federal screening standards as Medicare. This includes background checks, credentialing, and everything like that.
➜ Some states are easygoing and don’t ask for extra screenings if you’ve already been screened by a different state. But some might still require you to go through the same steps as in-state providers.
➜ You can get paid back for emergency services you give to Medicaid beneficiaries. This makes sure patients receive care on time, even if they’re away from their home state.
➜ If you have Medicaid’s prior approval, you can also get paid back for non-emergency services. This covers treatments and procedures that have already been approved.
➜ If some medical equipment or devices aren’t available in the patient’s home state, you can sign up to offer these important services.
Step #2: Get Your National Provider Identifier (NPI)
The NPI is a unique 10-digit number for identifying healthcare providers. You’ll need it to apply for and bill Medicaid.
If you don’t have an NPI yet, simply go to the NPPES website and apply online. The application is straightforward – just provide some basic personal and professional details.
If you’re in a group practice, make sure your group has its own NPI number too. Each provider and the group itself needs a distinct NPI.
Once you have your NPI, keep your information current on the NPPES website. Update anything that changes – your practice location, contact info, credentials, etc. Accurate details ensure smooth billing and communication with Medicaid.
The NPI application process is quick and easy. Just set aside a few minutes to get this essential ID number. Then you’ll be ready to move forward with Medicaid provider enrollment.
Step #3: Complete and Submit the Medicaid Provider Enrollment Form
After obtaining your NPI, it’s time to fill out the Medicaid provider enrollment application for your state. This crucial step registers you as a Medicaid provider.
- First, go to your state’s Medicaid website and download the provider enrollment form. For example, here is New York State’s form.
- Next, carefully complete the entire application. Provide your personal and practice details like name, address, contact information, professional credentials, services offered, and more.
- Also include important billing details like your Tax ID Number (TIN).
Double check that all information is accurate before submitting the form.
Step #4: Complete Background Checks and Fingerprinting
Most states require Medicaid providers to undergo background checks and fingerprinting. This ensures you have no criminal history that could risk patient safety.
To complete this step:
- Run background checks on yourself to verify your history. Disclose any past issues upfront.
- Get fingerprinted. This allows the state to cross-check your identity against criminal databases.
- Comply with all background check requirements mandated by your state. Different states have different rules. But full compliance is key.
- Be patient. Background checks can take time to process. Stay in touch with the state to move it along.
- Disclose everything. Trying to hide past problems will only delay or derail your application. Honesty and transparency are vital.
The background check process protects patients. Embrace it as an important part of credentialing. Complete this step fully and correctly. That gets you one step closer to serving Medicaid members.

Step #5: Get Ready for Review and Inspection
Once you submit your Medicaid application, the state Medicaid office will take a close look at your application and documents. They may also conduct an on-site inspection of your practice.
Take this time to get ready and collect any extra information the Medicaid office might need to help process your application easily. If asked, be ready to give more documents.
The inspection will verify that your facilities, operations, and patient records meet state regulations. Inspectors might visit your office, check compliance procedures, and look over patient files.
This step makes sure your practice follows Medicaid care standards. This is your chance to show that you have the staff, equipment, and procedures to provide quality healthcare services to Medicaid patients. Approach it as an opportunity to showcase your readiness. Dealing with any possible problems ahead of time will make acceptance easier.
Step #6: Get Your Medicaid Provider Number
After your Medicaid application gets the green light, you’ll get your own Medicaid Provider Number (MPN). This ID number is important for filing claims and getting paid for treating Medicaid patients.
Once you’re approved, you’ll get an email or a letter letting you know that you’ve been credentialed. With this notice, you’ll receive your new MPN.
➜ If you have an MPN, you can begin billing Medicaid and get paid back for your services. This is the last step to become an authorized Medicaid provider.
➜ If your application is delayed, make sure to check in with the Medicaid office quickly. Keeping track of the process can help fix problems and speed up approval.
➜ Approval times can change depending on the state, but they usually take about 30 to 60 days after you submit a complete application.
Now that you have your MPN, you can start treating Medicaid beneficiaries and getting paid back. This milestone shows that your hard work to get credentialed has really paid off. Just remember, you need to keep your information up to date to keep your Medicaid billing privileges active.
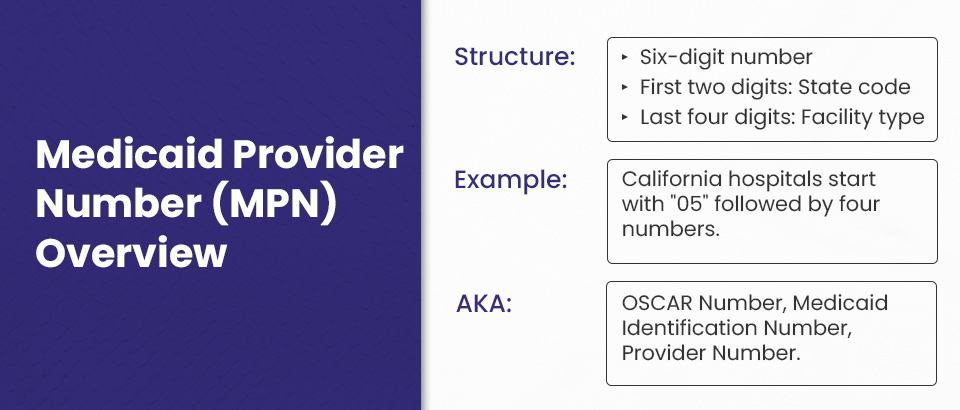
💡 What is the Medicaid Provider Number (MPN)?
The Medicaid Provider Number (MPN) is a unique six-digit identifier assigned to healthcare providers participating in the Medicaid program. The first two digits represent the state where the provider operates, and the last four digits indicate the type of facility. For instance, California hospitals have MPNs that begin with “05” followed by four additional digits specific to the hospital.
The MPN may also be referred to by other names, such as the OSCAR Number (Online Survey, Certification, and Reporting), Medicaid Identification Number, or simply Provider Number. These terms are interchangeable and all refer to the same unique number used to identify Medicaid providers.
Step #7: Start Serving Medicaid Patients
Now that you have your Medicaid provider number, you can start offering healthcare services to Medicaid recipients. Here are some key things to keep in mind:
- Make sure to update your provider profile in the Medicaid directory. Include your correct contact info, service hours, and the services you offer. This makes it easy for patients to find you.
- Teach your staff about Medicaid policies, including how to check eligibility, handle billing, and ensure compliance. When everyone is on the same page, things run smoothly.
- Find out how to use your state’s Medicaid Management Information System (MMIS) to submit claims and check patient eligibility. Accurate training eliminates Medicaid billing problems.
- Before you provide services, make sure to check the patient’s current Medicaid eligibility using the state verification system. This keeps you safe from denied claims.
- Make sure to provide great care and keep an eye on how happy patients are. Improving things all the time makes the care experience better for Medicaid patients.
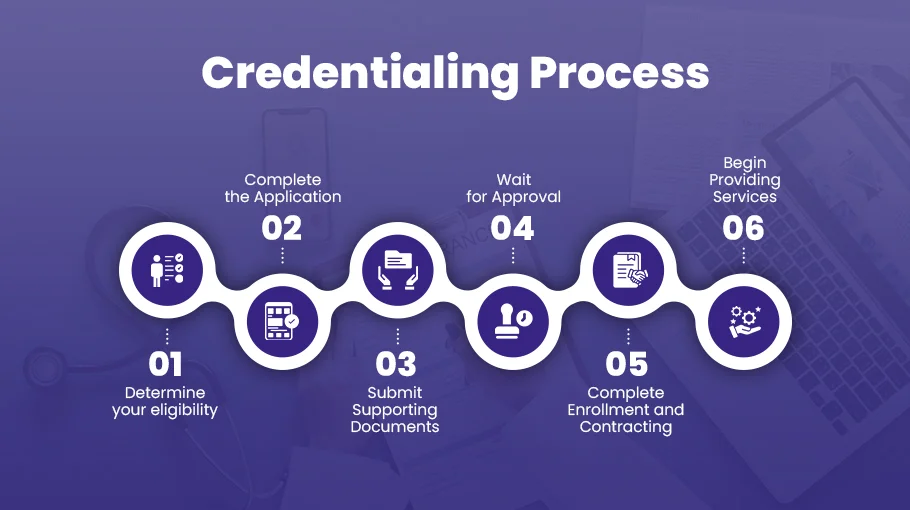
Just follow these steps, and you’ll be on track to serve the Medicaid population successfully while staying compliant and getting the best reimbursement.
The Significance of Medicaid Credentialing for Healthcare Providers
Getting Medicaid credentialing is a smart choice for healthcare providers who want to grow their services and reach a large market. As a Medicaid-approved provider, you can offer your expertise to a large segment of the population that relies on this government healthcare program for their medical needs.
Here are the main benefits of getting credentialed with Medicaid:
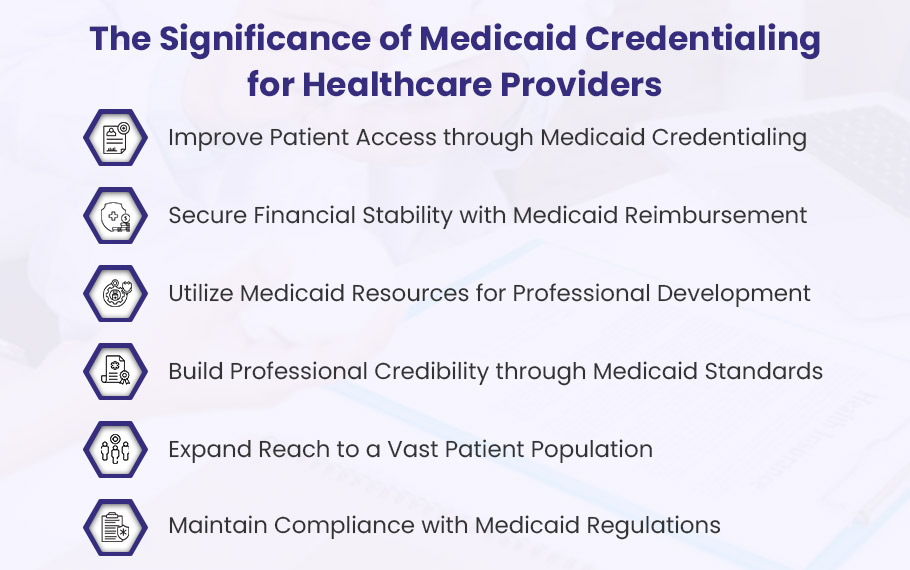
Expand Your Reach and Help More Patients by Accepting Medicaid
As a healthcare provider, joining Medicaid lets you truly help patients who need it most. Lots of people on Medicaid have a hard time finding doctors who take their insurance. By accepting Medicaid, you open your practice to a wider population in need of care. You can fill more appointment slots, run at full capacity, and reach out to serve patients from different areas and backgrounds. It means more patients can get the essential healthcare they need. Taking Medicaid can help your practice and support your goal of giving great care to all patients, no matter what kind of insurance they have.
A Steady Stream of Reimbursement Through Medicaid Credentialing
As a healthcare provider, it’s important to have a reliable source of payment to keep your practice financially healthy. Getting credentialed with Medicaid helps you get paid for the services you offer to Medicaid beneficiaries. This includes payment for office visits, hospital care, procedures, and other services. Medicaid reimbursement gives you a steady income, so you can concentrate on providing quality care without stressing about money issues. Medicaid provides a reliable way to get paid for taking care of your patients. Credentialing helps you access this important reimbursement support for your practice.
Gain Access to Valuable Training Resources
Getting credentialed with Medicaid gives you access to many helpful resources for professional development that can enhance your practice. Medicaid has training programs, webinars, and other chances for you to improve your skills and provide better care.
For example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) provides free online training modules and educational webinars to keep you up-to-date on the latest regulations, quality initiatives, and best practices. Using these Medicaid resources can help you easily access the tools and knowledge you need to improve your operations, try new care models, and get better results for your patients.
Build a Trusted Reputation through Medicaid Credentialing
When healthcare providers get credentialed with Medicaid, they show they are serious about meeting high-quality standards. Medicaid checks licenses, certifications, and backgrounds carefully. So, if you’re credentialed, it means you’ve passed their tough checks. This builds a reputation in the community as a trusted and reliable provider who is dedicated to delivering quality care. Patients can feel sure about picking a provider who is approved by Medicaid. A good reputation will bring in more patients looking for a provider they can trust. Getting credentialed with Medicaid shows that you meet high standards and boosts your professional reputation.
Gain Access to a Massive Patient Base
Medicaid lets healthcare providers reach and support underserved communities. Accepting Medicaid helps you connect with patients such as low-income families, pregnant women, children, and people with disabilities. You can really help those who need it the most. Taking care of these overlooked groups helps close the gap in healthcare and boosts the wellbeing of the community. This is your chance to make a bigger difference and achieve your goal of helping others. Helping more people and giving good medical care to those who really need it is possible with Medicaid credentialing.
Avoid Legal Troubles and Hefty Fines by Staying Compliant
As a Medicaid provider, it’s important to keep up with all the Medicaid rules and requirements. Having the right credentials makes sure you meet the standards for documentation, billing, and services. This keeps you safe from big fines, penalties, and legal issues later on. For instance, adhering to Affordable Care Act and Medicaid guidelines for services and documentation allows you to accurately submit claims and get paid for your work. Keeping up with credentialing helps you feel confident that your practice is running in an ethical and legal way.
How to Avoid Medicaid Credentialing Mistakes?
Credentialing mistakes can badly impact your healthcare practice revenue and your ability to provide care to Medicaid beneficiaries. Here are some key points that show how to avoid common credentialing mistakes with the Medicaid program.
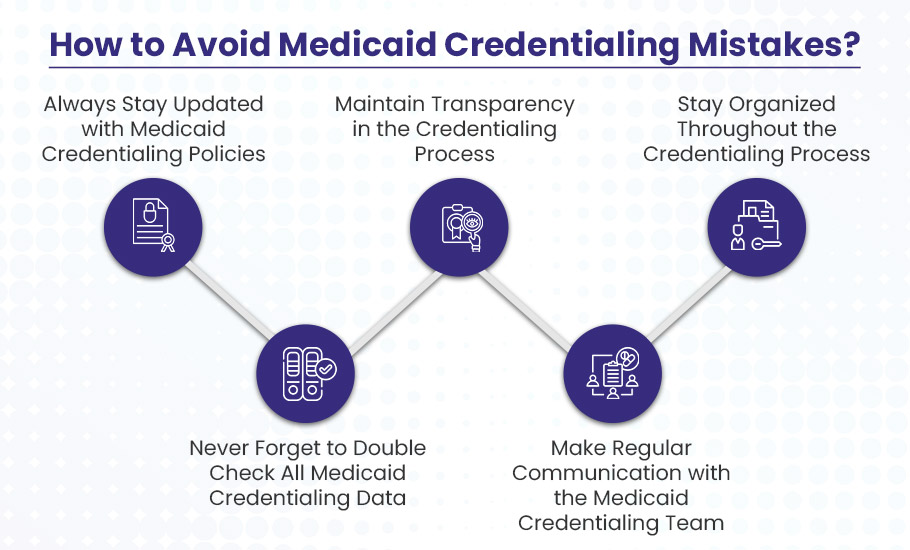
Always Stay Updated with Medicaid Credentialing Policies
Staying up to date with Medicaid credentialing policies is super crucial for healthcare providers to avoid costly mistakes. Otherwise, if you don’t follow the latest requirements, you might get your claims denied, lose your credentials, and even get kicked out of Medicaid programs.
Honestly, it’s simple to miss small changes in application processes, document standards, and eligibility rules. Medicaid policies change from state to state and keep evolving all the time. And if you miss an update, it could put your credentials and claims reimbursement in danger.
So, make sure to check your state’s Medicaid website often and sign up for email alerts. Oh, and don’t forget to bookmark the credentialing section and check out any new announcements. This little habit helps you stay updated on changes that affect providers.
By the way, tools like CAQH ProView are great for keeping track of compliance. The automated system keeps an eye on your credentials, license renewals, and expiration dates. Honestly, it’s such an easy way to stay on top of important deadlines you really need to meet.
Never Skip the Double-Check
Forgetting to double-check your Medicaid credentialing data can be a really costly mistake. Seriously, it can cause big problems for healthcare providers. Even just a small mistake or missing document can lead to rejected applications and long delays in getting approved. And until the issues are sorted out, you won’t be able to see Medicaid patients or get paid for the services you provide.
You see, you need to submit a lot of detailed information and documents for the credentialing process. It’s so easy to make a typo, skip a field, or forget a needed document when you’re handling a ton of paperwork. But, these small mistakes can totally slow everything down.
That’s exactly why it’s super important to check every piece of information carefully before you submit your credentialing application. Double-check spellings, dates, license numbers, certifications—you name it! Better yet, getting a colleague or a professional credentialing service like BellMedEx to look over your documents can help catch mistakes you might have missed.
In the end, if you put in a bit of extra effort at the start, you can avoid a big headache later. Plus, you’ll make sure you don’t miss out on Medicaid money while waiting to resubmit and get approved. So please, don’t let a simple mistake mess up your credentialing. Just double-check your data!
Maintain Transparency in the Credentialing Process
Be honest about your work history, qualifications or any disciplinary actions for a smooth credentialing process. If there have been gaps in employment history or any other issue, openly disclose these upfronts. Providing context and complete explanations can prevent any kind of misunderstanding and build trust with credentialing entities. Being truthful helps you to avoid any rejection or delays due to an error in your credentialing application.
Make Regular Communication with the Medicaid Credentialing Team
Effective and open communication with Medicaid entities can speed up the resolution with your credentialing process. You need to identify the right assistant in the Medicaid office who can help you to get timely updates and responses to all of your queries.
After submission of your application, it’s important to check the status regularly. If the Medicaid office requests additional information, respond immediately. Always open lines of communication to address any issue at the spot and keep the credentialing process moving forward.
Additional Tips for Successful Medicaid Credentialing
- Think about using credentialing management software or bringing in credentialing experts to make the application process smoother. These tools and professionals help automate tasks, track progress, and make sure all necessary documents are correct and submitted on time.
- Consider joining groups like the American Medical Association (AMA) or the National Association of Community Health Centers (NACHC). These groups offer important resources, guidance, and support to help you get through the Medicaid credentialing process.
- Do regular checks to make sure your practice follows Medicaid rules. These reviews keep records accurate and current, and they help spot potential issues before they turn into problems.
- Get to know the Medicaid appeals process just in case your credentialing application gets denied. It’s important to know the steps you need to take, the documents you have to gather, and the key deadlines to make your reapplication successful.