Patient privacy in healthcare has great significance. Healthcare providers need to maintain patient privacy. It is crucial to remain vigilant and updated with regulations to enhance and sustain patient privacy. This allows them to provide services without legal consequences and boost revenue growth. This article will discuss patient privacy, its importance, and the best ways to maintain it.
What is Patient Privacy?
Patient privacy refers to patients’ right to keep their personal and medical information confidential. This encompasses everything from medical histories, treatment records, contact details, and other data recorded during a patient’s visit or stay at a healthcare facility.

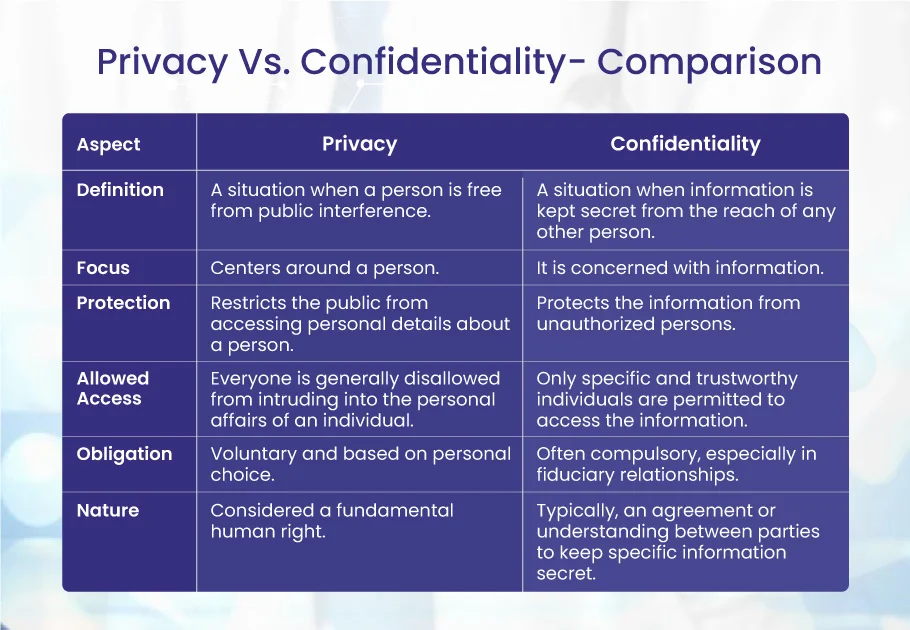
Privacy Vs. Confidentiality
The two words “privacy” and “confidentiality” are frequently used in opposition to one another. When we talk about confidentiality, it is professional. Privacy is personal or private, i.e., the range will be confined to oneself only—only those people whom the individual trusts will be included in the range. Only a few things separate the two concepts, but confidentiality is a more sophisticated version of Privacy.
Did You Know?

Why is Patient Privacy Important In Healthcare?
Patient privacy is essential to building confidence between patients and healthcare professionals and is not merely a moral issue. Stigmas can make it challenging for patients to get help and build relationships with professionals. Patients confident in doctors and health professionals are more likely to adhere to a treatment plan and program. Internet privacy is a significant worry for those who make online appointments, communicate with physicians via online messaging platforms like EHRs, and see clinicians during telehealth appointments.
When patients believe that their information is secure, they are more likely to:
Seek Medical Attention
Patients may avoid or delay seeking medical treatment if they fear their information might be disclosed.
Share Sensitive Information
Openness can lead to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment.
Adhere to Medical Advice
Trust in a healthcare provider can improve patient compliance with treatment plans.
Which Laws Govern Patient Privacy?
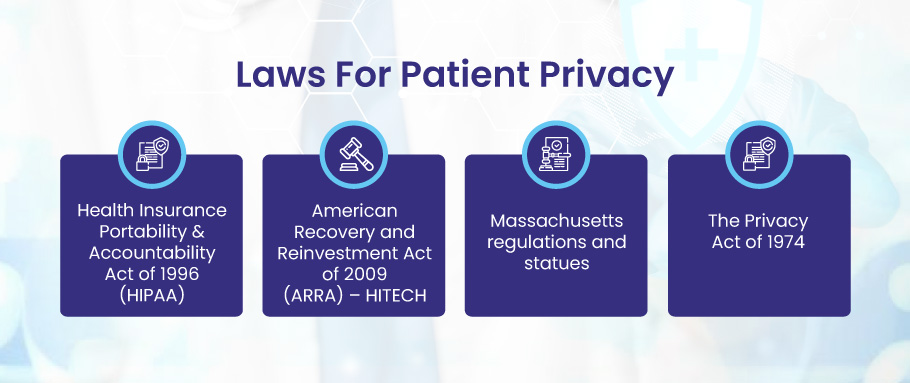
Several laws have been put in place globally to safeguard patient Privacy. In the U.S., the primary law governing patient privacy is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). HIPAA mandates the protection of patients’ personal and health information and sets guidelines on how healthcare providers can share this data.
What is Medical Identity Theft?
Medical identity theft is when someone steals or uses your personal information (such as your name, Social Security number, or Medicare number) to submit fraudulent claims to Medicare and other health insurers without authorization. Medical identity theft can disrupt your medical care and waste taxpayer dollars. In extreme circumstances, it could be life-threatening if the wrong information is in your medical record.
Here are the State and Federal Laws that Protect Patient Privacy
- Health Insurance Portability & Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA)
- American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) – HITECH
- Massachusetts regulations and statues
- The Privacy Act of 1974
Did You Know?
According to AMA, breaching HIPAA can result in hefty fines and, in extreme cases, imprisonment. It’s essential to regularly train staff on HIPAA compliance and the significance of patient privacy.
How Do You Maintain Patient Privacy in Healthcare?
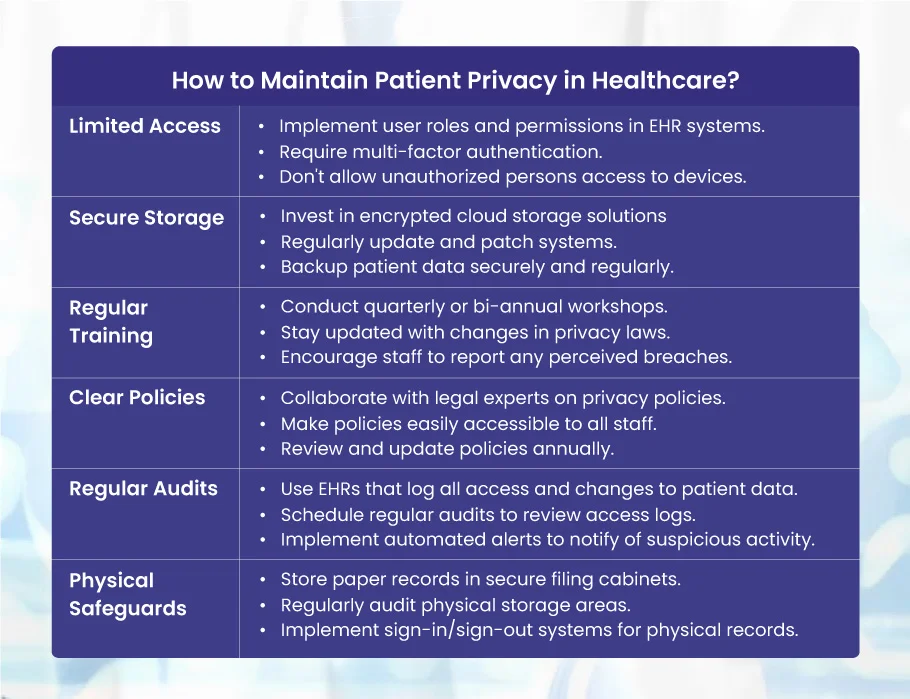
Maintaining patient privacy requires a combination of robust policies, regular training, and advanced technology. Here are some best practices:
Limited Access
- Implement user roles and permissions in electronic health record (EHR) systems. For instance, a receptionist might only need access to contact details and appointment times, whereas a physician would need access to medical histories.
- Require multi-factor authentication for accessing patient data. This could include something the user knows (password), something the user has (a secure token or smart card), and something the user is (fingerprint or retina scan).
- Allow authorized persons to access the area or devices with sensitive patient data and information. Additionally, don’t try to check and access the data in the presence of any person.
Secure Storage
- Invest in encrypted cloud storage solutions compliant with your country’s or region’s health data regulations (like HIPAA in the U.S.).
- Regularly update and patch systems to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Backup patient data securely and regularly, ensuring that backups are also encrypted.
Regular Training
- Conduct quarterly or bi-annual workshops on patient privacy. Include real-life scenarios and role-playing exercises.
- Stay updated with changes in healthcare privacy laws and update training material accordingly.
- Encourage staff to report any perceived breaches or questionable practices without fear of retaliation.
Clear Policies
- Collaborate with legal and compliance experts to draft comprehensive patient data handling and privacy policies.
- Make these policies easily accessible to all staff, and ensure they acknowledge in writing that they have read and understood them.
- Review and update policies annually to reflect any changes in technology or legislation.
Regular Audits
- Use EHR systems that automatically log all access and changes to patient data.
- Schedule regular audits (e.g., monthly or quarterly) to review access logs, looking for anomalies or unauthorized access.
- Implement automated alert systems to notify administrators of suspicious activity.
Physical Safeguards
- Store paper records in secure filing cabinets within rooms with restricted access, monitored by surveillance cameras.
- Regularly audit physical storage areas to ensure they’re secure and free of potential risks (e.g., being situated near water sources that might cause damage).
- Implement sign-in/sign-out systems for physical records so there’s a clear trail of who accessed a file and when.
Pro Tips to Maintain Patient Privacy

Final Thoughts
Patient privacy is an integral part of quality healthcare provision. Every healthcare provider, doctor, and practice should recognize its importance and implement stringent measures to safeguard it. Not only does it build trust with patients, but it also ensures compliance with laws that have been put in place to protect the rights of these patients. Remember, a patient’s trust is as vital as their health in healthcare. Prioritize it.





